time limit per test
2.0 s
memory limit per test
256 MB
input
standard input
output
standard output
Tamref love random numbers, but he hates recurrent relations, Tamref thinks that mainstream random generators like the linear congruent generator suck. That’s why he decided to invent his own random generator.
As any reasonable competitive programmer, he loves trees. His generator starts with a tree with numbers on each node. To compute a new random number, he picks a rooted subtree and multiply the values of each node on the subtree. He also needs to compute the number of divisors of the generated number (because of cryptographical applications).
In order to modify the tree (and hence create different numbers on the future), Tamref decided to perform another query: pick a node, and multiply its value by a given number.
Given a initial tree _T_, where _T__u_ corresponds to the value on the node _u_, the operations can be summarized as follows:
- RAND: Given a node _u_ compute
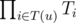 and count its divisors, where _T_(_u_) is the set of nodes that belong to the subtree rooted at _u_.
and count its divisors, where _T_(_u_) is the set of nodes that belong to the subtree rooted at _u_. SEED: Given a node _u_ and a number _x_, multiply _T__u_ by _x_. Tamref is quite busy trying to prove that his method indeed gives integers uniformly distributed, in the meantime, he wants to test his method with a set of queries, and check which numbers are generated. He wants you to write a program that given the tree, and some queries, prints the generated numbers and count its divisors.
Tamref has told you that the largest prime factor of both _T__u_ and _x_ is at most the Tamref’s favourite prime: 13. He also told you that the root of _T_ is always node 0.
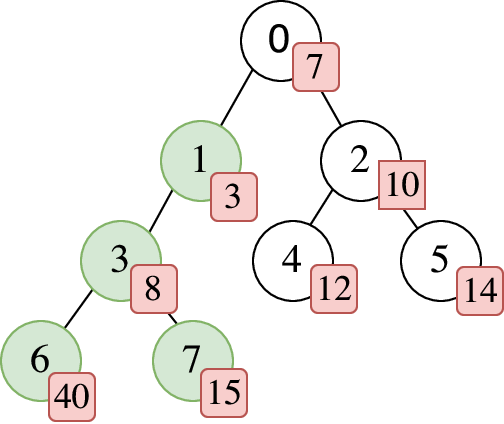
The figure shows the sample test case. The numbers inside the squares are the values on each node of the tree. The subtree rooted at node 1 is colored. The RAND query for the subtree rooted at node 1 would generate 14400, which has 63 divisors.
Input
The first line is an integer _n_ (1 ≤ _n_ ≤ 105), the number of nodes in the tree _T_. Then there are _n_ - 1 lines, each line contains two integers _u_and _v_ (0 ≤ _u_, _v_ < _n_) separated by a single space, it represents that _u_ is a parent of _v_ in _T_. The next line contains _n_ integers, where the _i_ - _th_ integer corresponds to _Ti_ (1 ≤ _Ti_ ≤ 109). The next line contains a number _Q_ (1 ≤ _Q_ ≤ 105), the number of queries. The final _Q_ lines contain a query per line, in the form “_RAND_ _u_” or “SEED _u_ _x_” (0 ≤ _u_ < _n_, 1 ≤ _x_ ≤ 109).
Output
For each _RAND_ query, print one line with the generated number and its number of divisors separated by a space. As this number can be very long, the generated number and its divisors must be printed modulo 109 + 7.
Example
input
Copy
1 | 8 |
output
Copy
1 | 14400 63 |
题意:建一颗树,查询 所有以当前节点和所有儿子节点因子个数,更新,单点更新倍数。
题解:首先dfs把所有位置出现的序 排好。题目样例 dfs,进入的先后顺序 是
s[0]=1,s[1]=2,s[3]=2,s[6]=4,s[7]=5,s[2]=6,s[4]=7,s[5]=8;
然后保留每个节点最后一个所覆盖的最大范围如:
e[0]=8, 因为 0节点覆盖了所有节点也就是 1-8 ,e[1]=5,1节点 覆盖了所有序从 s[1]-e[1](2 - 5)的节点。
然后以序建一颗线段树:
查询: x 每次查询 [s[x],e[x]];
更新: x 每次更新 [ s[x] ,s[x] ];
我的线段树每次保存的是 (l,r] ,所以 l 每次要-1。
这题数据处理,每个节点保留所有素数因子个数,然后求的值就是所有素数的乘积,因子个数就是相应素数个数+1的乘积,
假如 素因子2有6个,素因子3有 2个 ,素因子5有2个,输出就是 2^63^25^2, 733
1 | #include<iostream> |
0